Geotextile Fabric: Enhancing Infrastructure and Protecting the Environment
Geotextile fabric, a versatile material often overlooked, plays a crucial role in modern construction and environmental conservation. This article delves into the types, applications, advantages, and future trends of geotextile fabric, shedding light on its diverse uses and environmental benefits.
Introduction to Geotextile Fabric
Geotextile fabric, essentially a synthetic material, is designed to enhance soil stability and provide support in various civil engineering projects. Its importance extends beyond conventional construction materials, offering a sustainable solution in multiple applications.
Types of Geotextile Fabric
Woven Geotextiles
Woven geotextiles are crafted through a weaving process, resulting in a strong and durable fabric. These are ideal for projects that require high tensile strength, such as road construction and retaining walls.
Non-woven Geotextiles
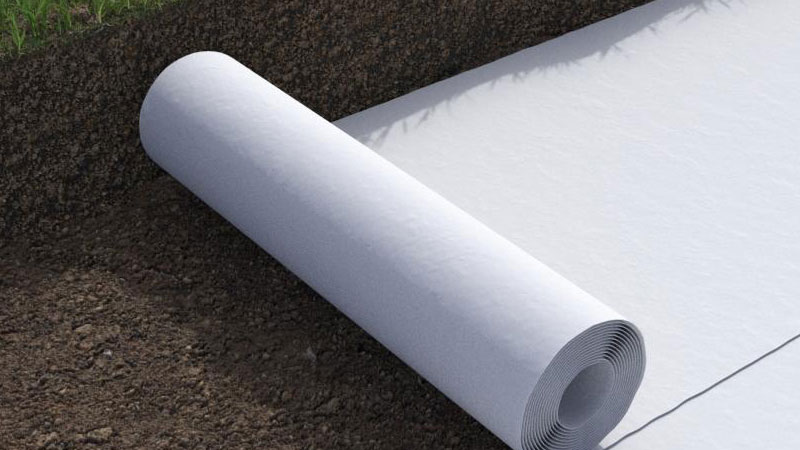
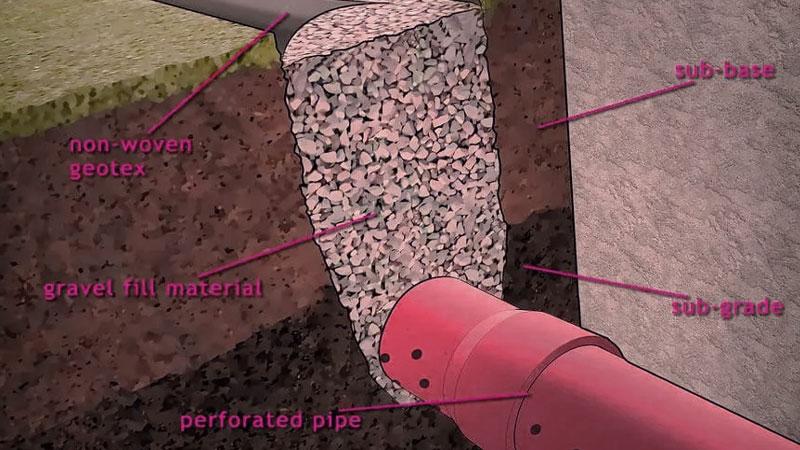
Non-woven geotextiles, on the other hand, are created through a bonding process, making them more porous. This type is commonly used in drainage systems and erosion control due to its ability to allow water flow while preventing soil erosion.
Knitted Geotextiles
Knitted geotextiles combine flexibility and strength, making them suitable for various applications. They find their place in projects requiring a balance of durability and adaptability.
- Applications of Geotextile Fabric
- Geotextile fabric finds application in a myriad of projects:
Road Construction
In road construction, geotextile fabric acts as a reinforcement layer, distributing loads and preventing soil erosion, ultimately enhancing the longevity of the road.
Erosion Control
The use of geotextile fabric in erosion control prevents soil displacement, preserving landscapes and protecting water bodies from sedimentation.
Drainage Systems
Geotextile fabric serves as a filter in drainage systems, allowing water passage while retaining soil particles, preventing clogging.
Retaining Walls
In retaining wall construction, geotextile fabric provides stability by reinforcing soil, reducing the risk of collapse and erosion.
Advantages of Using Geotextile Fabric
Strength and Durability
Geotextile fabric’s inherent strength and durability contribute to the stability of construction projects, ensuring long-term performance.
Environmental Benefits
The use of geotextile fabric aligns with environmental conservation efforts, minimizing soil disturbance and promoting sustainable construction practices.
Cost-effectiveness
Despite its advanced properties, geotextile fabric offers a cost-effective solution compared to traditional construction materials.
How to Choose the Right Geotextile Fabric
Choosing the right geotextile fabric involves understanding project requirements and specifications. Factors such as soil type, load-bearing capacity, and environmental conditions play a crucial role in decision-making.
Installation of Geotextile Fabric
Proper installation is paramount to the effectiveness of geotextile fabric. Site preparation, including clearing debris and leveling, coupled with correct installation techniques, ensures optimal performance.
Maintenance of Geotextile Fabric
Regular inspections help identify wear and tear. Timely repair or replacement, when necessary, ensures the continuous functionality of geotextile fabric in the long run.
- Geotextile Fabric in Environmental Conservation
- Beyond construction, geotextile fabric contributes to environmental conservation:
Soil Stabilization
Geotextile fabric aids in stabilizing soil, reducing the risk of landslides and preserving natural habitats.
Protection of Aquatic Ecosystems
In water-related projects, geotextile fabric prevents soil runoff, protecting aquatic ecosystems from sedimentation and pollution.
Case Studies
Exploring successful projects that utilized geotextile fabric showcases its positive impact on construction and the environment. Real-world examples demonstrate its effectiveness in diverse scenarios.
Common Misconceptions about Geotextile Fabric
Addressing myths and providing clarifications help dispel common misconceptions surrounding geotextile fabric, fostering better understanding and informed decision-making.
Future Trends in Geotextile Fabric Technology
The future of geotextile fabric technology holds exciting possibilities, with ongoing innovations and advancements that promise to further enhance its performance and applicability.
Environmental Impact of Geotextile Fabric
Examining the sustainability factors and recycling possibilities of geotextile fabric emphasizes its positive environmental impact, making it a responsible choice in construction projects.
Geotextile Fabric in Urban Planning
Integrating geotextile fabric into urban planning contributes to smart city development, offering sustainable solutions for infrastructure that align with environmental goals.
Expert Opinions on Geotextile Fabric
ndustry professionals provides valuable recommendations for various projects, helping decision-makers make informed choices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, geotextile fabric stands as a versatile and sustainable solution in construction and environmental conservation. Its diverse applications, coupled with environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness, make it a valuable component in modern projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is geotextile fabric used for?

Geotextile Fabric: Enhancing Infrastructure and Protecting the Environment
Geotextile fabric, a versatile material often underestimated, plays a crucial role in modern construction and environmental conservation. This article explores the types, applications, advantages and future trends of geotextile fabric, shedding light on its diverse uses and environmental benefits.
Introduction to Geotextile Fabric
Geotextile fabric, essentially a synthetic material, is designed to enhance soil stability and provide support in various civil engineering projects. Its importance extends beyond conventional construction materials, offering a sustainable solution in various applications.
Types of Geotextile Fabric
Woven Geotextiles
Woven geotextiles are manufactured using a weaving process, resulting in a strong and durable fabric. These are ideal for projects that require high tensile strength, such as road construction and retaining walls.
Non-Woven Geotextiles
On the other hand, non-woven geotextiles are created through a bonding process, making them more porous. This type is commonly used in drainage and erosion control systems because of its ability to allow water flow while preventing soil erosion.
Knitted Geotextiles
Knitted geotextiles combine flexibility and strength, making them suitable for a variety of applications. They find their place in projects that require a balance between durability and adaptability.
- Applications of Geotextile Fabric
- Geotextile fabric finds application in a myriad of projects:
Road construction
In road construction, geotextile fabric acts as a reinforcing layer, distributing loads and preventing soil erosion, thus increasing the longevity of the road.
Erosion Control
The use of geotextile fabric to control erosion prevents soil displacement, preserving landscapes and protecting bodies of water against sedimentation..
Retaining walls
When constructing retaining walls, the geotextile fabric provides stability by reinforcing the soil, reducing the risk of collapse and erosion.
Advantages of Using Geotextile Fabric
The inherent strength and durability of geotextile fabric contribute to the stability of construction projects, ensuring long-term performance.
Environmental Benefits
The use of geotextile fabric is aligned with environmental conservation efforts, minimizing soil disturbance and promoting sustainable construction practices.
Cost-effectiveness
Despite its advanced properties, geotextile fabric offers a cost-effective solution compared to traditional construction materials.
How to Choose the Suitable Geotextile Fabric
Choosing the right geotextile fabric involves understanding the project requirements and specifications. Factors such as soil type, bearing capacity and environmental conditions play a crucial role in decision-making.
Installation of Geotextile Fabric
Proper installation is critical to the effectiveness of the geotextile fabric. Site preparation, including debris removal and leveling, along with correct installation techniques, ensures optimal performance.
Maintenance of Geotextile Fabric
Regular inspections help identify wear and tear. Timely repairs or replacements, when necessary, ensure the continued functionality of the geotextile fabric over the long term.
Geotextile Fabric in Environmental Conservation
In addition to construction, geotextile fabric contributes to environmental conservation:
Soil Stabilization
The geotextile fabric helps stabilize the soil, reducing the risk of landslides and preserving natural habitats.
Protection of Aquatic Ecosystems
In water-related projects, geotextile fabric prevents soil runoff, protecting aquatic ecosystems against sedimentation and pollution.
Case studies
Exploring successful projects that have utilized geotextile fabric demonstrates its positive impact on construction and the environment. Real-world examples show its effectiveness in different scenarios.
Common Myths about Geotextile Fabric
Addressing myths and providing clarification helps dispel common misconceptions about geotextile fabric, promoting better understanding and informed decision-making.
Future Trends in Geotextile Fabric Technology
The future of geotextile fabric health holds exciting possibilities, with continued innovations and advancements that promise to further enhance its performance and applicability.
Environmental Impact of Geotextile Fabric
Examining the sustainability factors and recycling possibilities of geotextile fabric highlights its positive environmental impact, making it a top choice
Questions; What’s the difference between landscape fabric and geotextile fabric?
Landscaping fabric and geotextile fabric, although they share similarities, perform distinct functions in construction and landscaping projects. Let’s explore the differences between these two types of fabrics.
Landscape Fabric:
Landscaping fabric, often confused with geotextile fabric, is specifically designed for use in landscaping. Its main features include:
Weed Control:
Landscaping fabric is especially effective at controlling weeds, preventing their growth and spread.
Permeability:
It is generally permeable to water, allowing rainwater to reach the soil, maintaining adequate irrigation.
Aesthetics:
Designed to be aesthetically pleasing, it is often used under gravel mulches or in flower beds.
Geotextile Fabric:
Geotextile fabric, on the other hand, is more versatile in its applications and has specific characteristics for civil engineering projects. Key differences include:
Structural reinforcement:
Geotextile fabric is designed to reinforce structures and stabilize soil in construction projects such as roads and retaining walls.
Drainage:
Provides drainage properties, preventing water accumulation and preserving soil stability.
Use in Engineering Projects:
It is commonly used in civil engineering applications such as roads, railways and soil containment projects.
In summary, while landscape fabric excels in weed control and aesthetic appeal in landscaping, geotextile fabric is more focused on civil engineering applications, providing soil reinforcement and stability in a variety of projects.
Question: What is Type 3 geotextile fabric?
Type 3 geotextile fabric refers to a specific category of this material, with particular properties and characteristics suitable for certain applications. Let’s explore what defines Type 3 geotextile fabric:
Mechanical resistance:
Type 3 is known for its mechanical strength, being able to withstand considerable forces, which makes it suitable for applications where stability is crucial.
Permeability:
Maintains permeable properties, allowing the controlled passage of water. This characteristic is essential in projects involving drainage and water control.
Applications in Heavy Works:
Generally used in large-scale civil engineering projects, such as roads, railways, and other structures that require ground reinforcement and stability.
Soil Particle Retention:
Type 3 geotextile fabric is effective in retaining soil particles, preventing erosion and maintaining the integrity of the structure.
Durability in Demanding Environments:
Designed to withstand harsh conditions, Type 3 is durable and capable of maintaining its properties even in challenging environments.
Common Applications:
Road Construction and Paving:
Type 3 is often used as a reinforcing layer in road construction and paving projects, offering support and stability to the soil.
Soil Containment Projects:
In soil retaining structures such as retaining walls, Type 3 geotextile fabric plays a crucial role in preventing landslides and maintaining structural integrity.
Railway Infrastructure:
In railway projects, Type 3 is used to ensure soil stability under tracks and other infrastructure.
Erosion Control:
Its strength and particle retention capacity make it effective in controlling erosion on slopes and landslide-prone areas.
In short, Type 3 geotextile fabric is a fundamental choice in projects that require mechanical resistance, soil stability and water control, being widely used in civil engineering to guarantee the success of large-scale works.
Question: Does the geotextile fabric prevent water from passing through?
Yes, geotextile fabric has permeable properties, which means it allows the controlled passage of water. It does not act as a waterproof barrier, but rather as a filter that allows water to pass through it while retaining soil particles. This characteristic is especially beneficial in various civil engineering and landscaping applications. Let’s explore how geotextile fabric handles water:
Permeable Properties:
Controlled Drainage:
Geotextile fabric is designed to allow water to flow through it, which is crucial in drainage projects, preventing unwanted water accumulation.
Erosion Prevention:
In areas prone to erosion, geotextile fabric acts as a barrier against soil loss, while still allowing water to drain, preventing damage to the land.
Applications in Drainage Systems:
In drainage systems, geotextile fabric is often used to prevent blockages, allowing water to pass freely while trapping sediment.
Structure Protection:
When applied to containment structures, the geotextile fabric does not impede the passage of water, but helps maintain soil stability, preventing erosion that could compromise the structure.
Use in Hydraulic Projects:
In projects close to bodies of water, geotextile fabric is used to balance soil retention and permeability, contributing to the protection of aquatic ecosystems.
Conclusion:
In short, the geotextile fabric does not block the passage of water, but rather regulates and controls its flow. This makes it a valuable choice in a variety of contexts where it is necessary to balance soil stability with efficient water management in construction and landscaping projects.